Pros and Cons of Oil Heating – How Well Does It Perform Vs Alternatives

Kerosene, sometimes known as heating oil, is a liquid byproduct of refining petroleum.
Diesel is a close relative, but its chemical makeup is different, even though it has the same properties. Heating oil has a global market. For instance, it’s called kerosene oil in Asia and heating oil in the UK and the US.
There are different ways to use it, including producing electricity, lighting homes, and preparing meals. Its popularity typically peaks in the winter due to seasonality. Oil-fired boilers often heat water for a home’s central heating system, hot water radiators, and showers.
This comprehensive article contains more details that will inform you about heating oil.
Overview
Heating oil, against popular belief, is clean, safe, and readily available. Heating your home with something biodegradable and 95% cleaner than in the past is a perfect way to save expenditure and reduce your carbon footprint.
This article will explain why modern heating oil is risk-free, eco-friendly, and effective. We’ll also show you how heating oil fits into a bigger plan to help you reduce your family’s carbon footprint and meet their comfort needs.
Types of Heating Oil

Heating oil is available in a wide variety compared to other oils and fuels. More and more people are choosing options with less sulfur, and most agree that using cleaner oil will make machines last longer and work better. The various types of heating oil include:;
Gas oil
Often known as “red diesel,” gas oil is commonly used as a heavier fuel in older systems. Among the other choices, this one is the dirtiest.
Kerosene
Kerosene is widely used as a household and commercial heating oil. It’s inexpensive, burns cleanly, and is widely available. Popular with buyers due to its low cost, this option dominates the market.
Kleenburn kerosene
Compared to regular kerosene, this heating oil produces significantly less pollution when burned. The price of Kleenburn kerosene may be higher than that of regular kerosene. Still, it is far safer for the environment and helps keep emissions low, which is especially beneficial for businesses.
Furnace fuel
Municipal buildings, such as schools and universities, sometimes necessitate furnace fuel. It meets all the requirements and approved standards for heating oil. It is suitable for use in any industrial boiler.
What Are the Different Types of Oil Heaters?
Direct Oil Heater
In a hurry and need a lot of heat? No problem, turn to your handy direct oil heater. They function best in large, open spaces with plenty of ventilation, such as warehouses and factories. When it comes to direct heaters, master models are the gold standard in terms of performance, durability, and user-friendliness.
Direct oil heaters use the fuel slightly differently than indirect oil heaters, which also use oil. Instead of lighting the fuel and letting it burn, direct oil heaters light it and let it burn before sending the heat out with the fuel.
However, due to this, these heaters cannot be used in enclosed spaces with flammable materials. An essential part of any direct oil heater is its ventilation system. The heating process adds moisture to the air, rendering the heater useless for drying.
Indirect Oil Heater
Indirect oil space heaters are the best for warming up a large space. An indirect oil heater, like any oil heater, burns oil to produce large amounts of heat in locations without access to electricity.
They work best in enclosed spaces like stores, event tents, and exhibition halls, where air circulation is restricted. Flexible hoses provide for quick and easy distribution of warm air.
Diesel oil is fed into a combustion chamber and burned at a controlled rate, producing vast amounts of clean, safe, and dry heat. That makes them perfect for drying a building after a flood or heating a room. Despite this generalization, there is a wide variety of oil heaters available.
The main advantages of indirect heating are as follows:
- Because the boiler’s location doesn’t need to be close to any end users, it improves safety and mitigates danger.
- Direct heating systems are less adaptable than indirect heating systems. That is because of the need for a fuel supply for each point of consumption and a combustion gas vent for each consumer item.
- Indirect heating is more efficient since the boiler operates at peak efficiency. Direct heating has to work with the specifics of the consumer appliance to get combustions that are only sometimes ideal.
- It can use the same heat carrier and the system for heating and cooling if necessary.
- Sub-networks of hot water, hot air, or steam can be created using heat exchangers.
- Considering that the boiler is the only home part where temperatures become quite high, it makes sense to use less insulation there. In the event of a high volume of customers, this is of paramount significance.
Infrared Oil Heater
An infrared oil heater combines the efficiency of a mains-powered infrared heater with the power of an oil heater. That makes a powerful infrared heater that doesn’t need extra air conditioning.
As a result, they are perfect for defrosting machinery or pipes, warming up workspaces, and drying walls without creating dust. Also, since they focus on warming people and things rather than the air, they are much more efficient than traditional oil heaters.
Is a House With Oil Heating Worth Buying?

Oil-heated homes are very common in many parts of the world. Oil is often used to heat homes because it is cheap, easy to get, and has a high rating for safety.
Still, natural gas is more challenging to get to some places because of various factors. If you want to find out why oil heating is advantageous, here are the tips.
It is widely available
There are thousands of heating oil suppliers in many parts of the world. Whenever you need to place an order for heating oil, you are assured of obtaining the best price possible.
It is cost-effective
Heating oil is a great choice because it produces a lot ofmuch heat for the money. Oil prices have dropped significantly over the past decade, allowing homeowners to shop for the best deal.
If you don’t sign up for automatic delivery, this competition will maintain oil prices as low as possible.
But if you choose to have your heating oil delivered automatically from a single company, the price per gallon will go up. That may save you time, but it will cost you a lot of money.
It is efficient
There are 138,500 BTUs in one gallon of heating oil (BTUs are a unit of heat). Taking into account that the average efficiency of a burner is 85%, this means that it can produce 117,725 BTU per gallon.
Similarly, the BTU output of one gallon of propane is only 91,500. The effective BTU output per gallon drops to 86,925 with a 95% efficient burner.
It takes 1.35 gallons of propane to make the same amount of heat as one gallon of heating oil.
It is safe
The flash point of heating oil is 140 degrees Fahrenheit. As a result, it cannot even sustain a flame at normal temperatures.
That’s why it’s completely risk-free to keep in your house, unlike similar products. Heating oil needs to be heated and then atomized to be ignited.
Oil heat is a reliable, affordable option for indoor heating. When comparing heating oil and propane, heating oil is the superior choice. Besides its low price, natural gas also requires minimal upkeep.
Thanks to the availability of many vendors, you may shop for the best price on heating oil. Using comparative shopping platforms, you can get oil as you need it from different suppliers.
You can also install a Smart Oil Gauge to check the level of heating oil in the tank from your phone.
Pros of Oil Heating

Better for Heating Large Spaces
Oil-filled heaters generate more heat than a conventional space heater while consuming less energy. Indeed, it takes a little longer to get a nice toasty room, but once they do, they keep it that way for much longer and with far less energy.
You can save even more money on heating costs and increase the period between oil delivery by using additional heating equipment, like an electric space heater.
Safety
Many individuals believe that all oils are combustible. However, the oil for heating your home is just as safe as water.
You can’t strike a match and have it light a vat of heating oil. Instead, you need a special mechanism in many modern furnaces called an “advanced burning system.”
Even before the air reaches, harmful amounts of carbon monoxide, soot smells, and smoke is emitted by home heating oil.
Also, home heating oil vapors are not lethal, so if there is ever an emergency, you will have a greater chance of figuring out what’s wrong.
No Carbon Monoxide
Burning oil in a boiler results in carbon monoxide emissions, as with any fossil fuel. Boilers make carbon monoxide, but the flue takes it away from the boiler and your home. Carbon monoxide might enter the home if the flue is obstructed.
When turned off, your oil boiler will not burn fossil fuels and so will not emit carbon monoxide. If you suspect a leak, turn off all electricity to the house.
Consider turning off all appliances and having an oil boiler expert come and inspect them all rather than risk finding out which one is leaking and having to fix it.
Ideal for Remote Locations
Another of home heating oil’s primary benefits is how portable and easy it is to get to. If your home is in a remote rural or forested area or your community doesn’t have access to natural gas, you can use oil heat instead of natural gas.
You won’t have to rely on your community’s natural gas utility for heat because you’ll be in charge of the system and the gas supply.
Having an oil furnace and oil containment unit on your property is all that is required. You can have your system with just the addition of fuel.
Great for Regions With Colder Weather
Compared to other ways to heat your home, heating oil is cheaper and better for the environment.
Misconceptions about heating oil heat are often based on old ideas about how dirty modern fuels are or how inefficient older heating systems are.
Compared to natural gas, heating oil burns more quickly and efficiently, making it a more attractive home heating option.
Not only do oil furnaces use less fuel, but they also burn hotter, so fewer condensation forms than with gas or electric furnaces. That also increases the lifespan of the furnace.
Properly maintained oil furnaces can last 30 years or more, but heat pumps typically only last 12-15 years.
Lasts up to 30 Years With Proper Maintenance
Whether you use oil, propane, electricity, or natural gas, replacing your heating system can be expensive.
Oil-based heating systems can last for at least 30 years, and oil storage tanks can last up to 10 years longer than propane or natural gas tanks.
New low-sulfur oils are gentler on oil heating systems and call for less frequent, less intensive maintenance.
As a result, they can help extend its lifespan even further with appropriate upkeep. That is a huge improvement compared to natural gas systems, which can last half as long at most with proper care and even less without.
Can Be Stored Outside the Home
Tanks that store home heating oil are usually in the basement, but they could be elsewhere on the property.
That can be above the ground or underground. The normal capacity of an oil tank is 900 liters. However, the environment and your health are at risk when oil leaks or spills occur.
An oil spill can contaminate the groundwater and eventually make its way into the rivers and lakes where people get their drinking water.
An oil spill is not only dangerous because of the oil itself but also because it can cause unpleasant odors, fires, and explosions. The Technical Standards and Safety Act states that heating oil tanks must be in good shape.
Decentralized Distribution
There is a lot of heating oil on the market now, but there is little demand for it. Because more people want to heat their homes in the winter, it needs more resources.
The heating oil you need is available, unlike natural gas and propane, which can run out during the coldest months of the year.
A natural gas furnace requires a home to be located in a service area where the fuel can be piped to the building. However, oil furnaces can be utilized almost everywhere, as long as a fuel tank is present.
Indicates Malfunction Early
Oil-burning furnaces are reliable, despite their complexity. The good news is that many typical issues are simple enough for homeowners to fix.
However, you should bring in an HVAC expert for more complicated problems.
Lower Up-Front Costs
Many households are reluctant to switch to oil heating since they are used to paying a flat rate for natural gas each month.
During the winter, heating costs increase because most of a home’s oil is used in just three or four months. This rapidly rising cost has the potential to deter many potential buyers.
On the other hand, heating oil suppliers offer payment plans that can fit almost any budget. To avoid a large, unexpected oil bill at the end of the year, you can spread your oil payments out for the year and pay an average price.
When paid weekly or for two weeks, oil heating costs can be much lower than the average gas bill.
Cons of Oil Heating
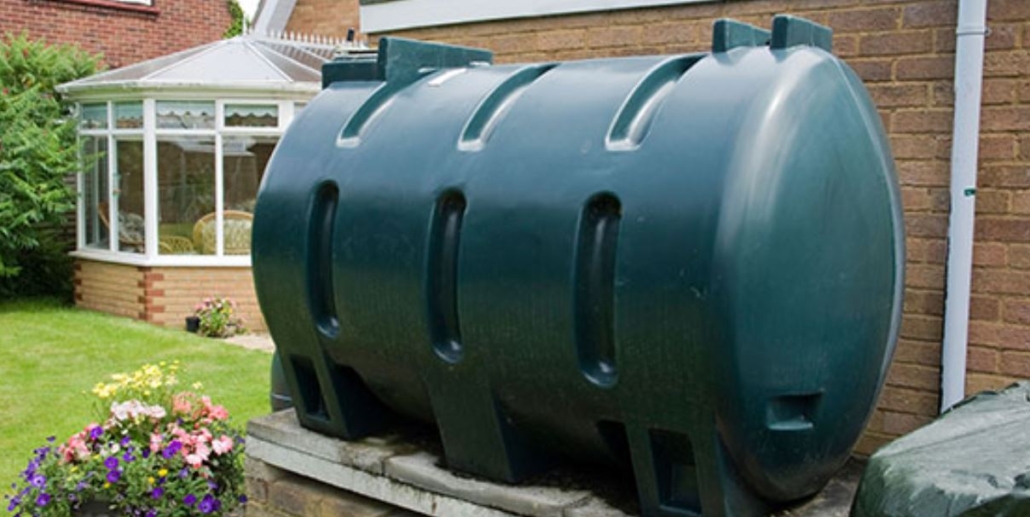

More Expensive Running Costs
The size and efficiency of your home will have a direct effect on your monthly costs. Smaller ones typically use less when comparing the amount of oil needed to heat different-sized homes.
More Maintenance
Many issues, such as soot buildup, are common in oil furnaces. If you don’t take care of your burner, it could get clogged, produce fumes, or cause “puff backs.” Heating systems that use gas or electricity are much less likely to need repairs.
Requires Additives
The compounds in heating oil additives increase the fire rate of your tank. Some things about fuel, like how thick it is and how hot it needs to be to start, can be changed by adding additives.
Need to Ensure Your Supply Doesn’t Run Out
If you wanted to know how much oil you had left in your tank, you had to dip a stick into the tank physically. That would cause a frenzy of terror if you’d forgotten about it for too long.
Install a watchman sensor in your oil tank to avoid running out.
It sends information about the level to a receiver that you can plug into a wall outlet in your home or office. A warning icon will appear on the receiver when your oil level falls below a certain percentage.
The Price of Oil Fluctuates
A gas or electric heater will likely cost less over time, although the initial investment in an oil heater could be lower. That’s because oil prices fluctuate much more and are generally higher than natural gas prices.
Oil prices and delivery fees spike in the winter compared to the rest of the year.
Requires an On-Site Storage Tank
The wiring and pipes that bring electricity and natural gas to your house connect to the larger distribution system.
If you heat your home with oil, you’ll need to install a tank on your property and keep it stocked with fuel.
May Be Noisier Than Gas
While certain sounds from your oil burner are quite natural, others, such as a deep rumbling, could signify difficulty and danger. Some may say that an oil burner is pulsing or pulsating instead of making a rumbling sound.
Nonetheless, consider the noise aspect before installing an oil heating system.
The Heating Oil Tank Can Also Be Unsightly
The position of your tank should be accessible for deliveries from far to prevent leaks. That may only sometimes be the most convenient option, but it’s something that some careful landscaping can fix.
Needs Plumbing Work to Allow Acidic Condensate Liquid to Drain Away
You will always need qualified and reliable plumbers to work on your gas boilers and central heating systems. That will ensure safe installations and maintenance for optimal performance.
Cannot Be Included in the HVAC System
One of the main reasons why gas and electric furnaces shouldn’t be used is that many of them are not built into HVAC systems. In places where summers are hot and winters are cold,
HVACs are very useful because they keep your home at a comfortable temperature all year. However, oil furnaces are stand-alone systems, so if you also want air conditioning in the summer, you’ll need to invest in a separate system.
Governments Want to Phase Out Oil
Many governments plan to stop installing new gas and oil boilers to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. They help homeowners pay for low-carbon heating systems to reduce prices and promote innovation.
Common Problems of Oil Heating and Solutions
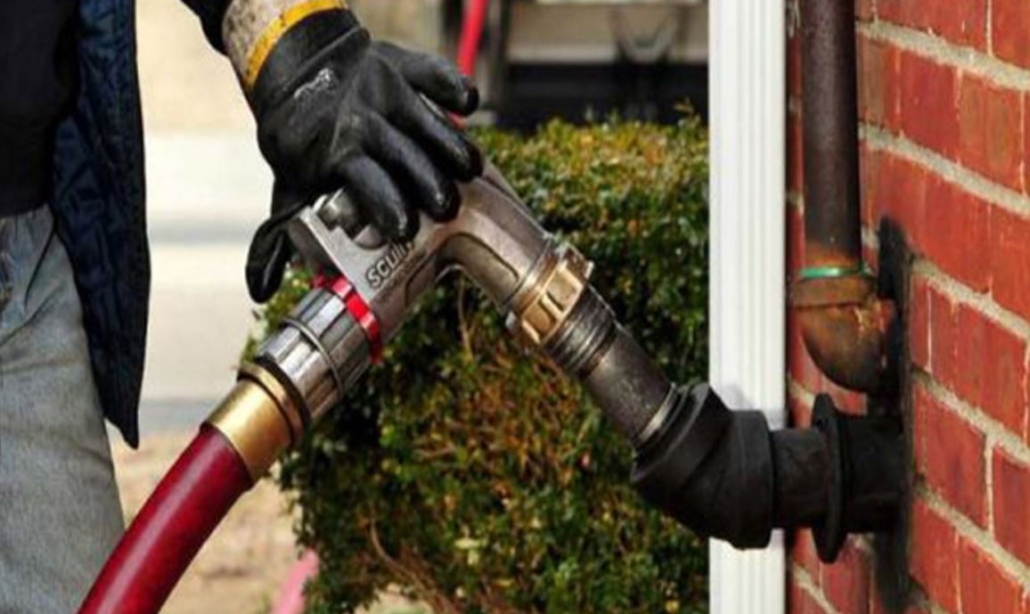

Leakage
The oil tank, pipelines, pipe fittings, valves, attachments, and filters can all be sources of oil leaks. Check these pieces out very carefully. Oil smudges or spills are a telltale symptom of an oil leak. If the oil storage tank is underground, a technician should check the oil burner to see if it is contaminated with water.
Won’t fire up
There may be a need to reset the furnace. The gas valve or a faulty thermostat connection could also be a problem. You should double-check the furnace’s control buttons and switches and click “Reset.”
However, this should only be done twice, as doing it more often could lead to oil backing up and catching fire.
Fires up and then stops
Low fuel and a clogged air filter are the potential reasons for this issue. Confirm if the thermostat is set properly by checking its settings.
If you need clarification on the default configurations, check the user guide. Also, check the gasoline tank to get an accurate reading of fuel levels.
Producing smoke
If your furnace doesn’t get enough air or has a warped or broken gasket, you may need to fix it. Ensure the combustion chamber is cool enough.
A blocked chimney, flue pipe, nozzle, end cone, or heat exchanger might overheat your furnace and produce smoke.
Burning excessive fuel
That could be due to a clogged air filter or a broken fan belt in the supply fan. Ductwork issues are another possible explanation. Check the filter first. Replace it as soon as it becomes blocked with dust or dirt.
If the filter seems OK, check the supply fan and belt. The fan belt frequently wears out and needs to be changed.
Making noise
Knocking sounds usually indicate that air has entered the lines. “Bleeding” is the solution to this.
It’s a simple fix, but a beginner might need help, and the way to do it might change depending on what your furnace burns. Refer to the instruction manual or consult a professional if unsure how to proceed.
Strange odors
Odors from out of the ordinary can have various origins. Nozzle, chimney, and heat exchanger blockages are the most common causes.
The first step is to clean them if they are dirty, then inspect the heat exchanger and the nozzle for any signs of damage.
Won’t heat on one floor
An air vent may have been blocked. First, check the air vents. The airflow from only some vents and not others may show a blockage. Consult a professional if you cannot determine the root of this problem.
Who Should Use Oil Heating?
Most homes use heating oil during the colder months as their main heat source. Heating oil is also used in commercial water heating systems and combined heat and power plants.
Oil Heating – FAQs

Q: How Long Can You Keep Heating Oil?
The straightforward answer to that question is 18–24 months. Don’t fret if you’re worried about not utilizing all your fuel in a single heating season. You can store it during the warm months and use it effectively once winter rolls around.
Q: How Much Heating Oil Should You Use in a Month?
Residential heating oil use varies widely from season to season due to ambient temperature. Two gallons of oil daily will be needed if the temperature outside is about 50 degrees.
At 15 degrees Fahrenheit or lower, you could need up to 8 gallons of heating oil daily. On the low end, that means 60 gallons per month, and on the high end, 240 gallons per month.
Q: How Much Heating Oil Do You Burn in an Hour?
Your heating oil consumption is determined by the living space of your home and the average time per day your furnace is on. An oil-burning heater uses an average of between 0.80 and 1.70 gallons of fuel per hour.
If your one-bedroom home uses a 300-gallon tank, and your furnace runs for 10 hours daily, you will need to refill your tank every 17 days.
Q: How Much Oil Does a House Use per Day?
From the previous answer, an oil-burning heater uses an average of between 0.80 and 1.70 gallons of fuel per hour. That equals 19.2 to 40.8 gallons per day in your one-bedroom home.
Q: Why Is My Heating Oil Burning So Fast?
How much heating oil your home needs depends on many things. These can be the number of people living there, the season, the average temperature where you live, and more.
Additionally, it can be unseasonable weather, poor insulation, or inefficient heating systems.
Q: How Long Should 500 Liters of Oil Last in Winter?
At 15 degrees Fahrenheit or lower, you could use up to 8 gallons of heating oil daily. That translates to 240 gallons per month, meaning a 500-gallon tank could serve you for two months.
Q: How Can I Make My Heating Oil Last Longer?
Here are some tips if you’re concerned about running out of heating oil or want to make the most of what you have.
- Use premium heating oil.
- Service your boiler regularly.
- Do an energy inspection of your home.
- Adjust your thermostat.
- Insulate your walls and floors.
- Heat Oil Monitors.
- Buy your heating oil when prices are lower.
Conclusion

With this information at your disposal, it is up to you to decide what type of furnace is best for your home.
If you can’t access natural gas lines, consider getting an oil heater. Still, HVAC systems are more practical than oil furnaces because oil furnaces are expensive to buy and maintain.